Ciutats: pedra sobre paper/ Cities: stone on paper
Qm Primavera 2014-2015
| Qm | Nivell Quadrimestral | Núm. màxim d'estudiants |
Idioma |
| P | 7-10 | 20 | "English only. Native or proficient english (B2 according to MERC) to be proven upon registration to the seminar" |
| Codi | Crèdits | Distribució (T,P,L) | Departament | Tipus | H/s treball estudiant |
| 290174 | 4 (3,5 ECTS) | 2T, 2L | OUT | Opt | 3 hores |
| Dia | Horari | Núm. de setmanes |
| Dilluns/Monday | 15:30-17:50 | 12 |
| Dimecres/wednesday | 15:00-16:00 | 12 |
| Professor responsable | Adolf Sotoca |
Objetiu
|
El objetivo de este curso es capacitar a los estudiantes a construir con cualquier dibujo 2D perspectivas de software, perspectivas forzadas, proyecciones distorsionadas y trompe l'oeil.
Estas técnicas se utilizan hoy en día en los comerciales (ver http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UelJZG_bF98), en el arte de la calle (ver: http://www.julianbeever.net/), paisaje urbano (véase: http :/ / www.varini.org/) o incluso en estudios en neurociencias (ver http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gJhyu6nlGt8). En el pasado, el arte ha utilizado este conocimiento desde el Renacimiento hasta el siglo XX (ver, entre muchas otras: http://www.mcescher.com/ o http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Ambassadors_ (Holbein) .
La consecuencia de estos estudios para la educación de los estudiantes consistirá en una importante mejora de sus habilidades espaciales.
“Cities: stone on paper” tracta dels arquitectes que escriuen sobre les seves ciutats. Sis urbs exemplars (3 europees i 3 americanes) són el camp de treball a partir del qual els participants en el seminari obtindran una visió rica i global de l’aproximació arquitectònica a la ciutat. |
Objetivo
|
El objetivo de este curso es capacitar a los estudiantes a construir con cualquier dibujo 2D perspectivas de software, perspectivas forzadas, proyecciones distorsionadas y trompe l'oeil.
Estas técnicas se utilizan hoy en día en los comerciales (ver http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UelJZG_bF98), en el arte de la calle (ver: http://www.julianbeever.net/), paisaje urbano (véase: http :/ / www.varini.org/) o incluso en estudios en neurociencias (ver http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gJhyu6nlGt8). En el pasado, el arte ha utilizado este conocimiento desde el Renacimiento hasta el siglo XX (ver, entre muchas otras: http://www.mcescher.com/ o http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Ambassadors_ (Holbein) .
La consecuencia de estos estudios para la educación de los estudiantes consistirá en una importante mejora de sus habilidades espaciales.
“Cities: stone on paper” trata de los arquitectos que escriben sobre sus ciudades. Seis urbes ejemplares (3 europeas y 3 americanas) son el campo de trabajo a partir del cual los participantes en el seminari obtendran una visión rica y global de la aproximació arquitectónica a la ciudad. |
Subject abstract
|
"Cities: stone on paper" focuses on architects who write about their cities. A set of six remarkable case studies (3 European + 3 North American) constitutes the field from where the students will obtain a diverse and rich overview of the architectural approach to he city scale.
We will get to know them through six seminal books written by architects:
Barcelona: “Cerdà / Ensanche” by Manuel de Sola‐Morales.
New York City: “Delirious New York” by R. Koolhaas.
Los Angeles: “Los Angeles: the architecture of four ecologies” by R. Banham.
Berlin:“Berlin as a green archipelago” by O.M. Ungers.
Boston: “The Image of the City” articles by K. Lynch
Rome: “An eternal city. Four lessons of twenty-‐seven centuries” by L. Quaroni
|
Learning outcomes. At the end of the course the student should be able to:
|
Generic required and trained competences.
- Reading and understanding of text. - Capability for translating reflections into graphics. - Capability for synthesis of reflections in brief but meaningful texts. - Basic culture on urbanism through the analysis and reflection of paradigmatic case studies of western cities urban history.
|
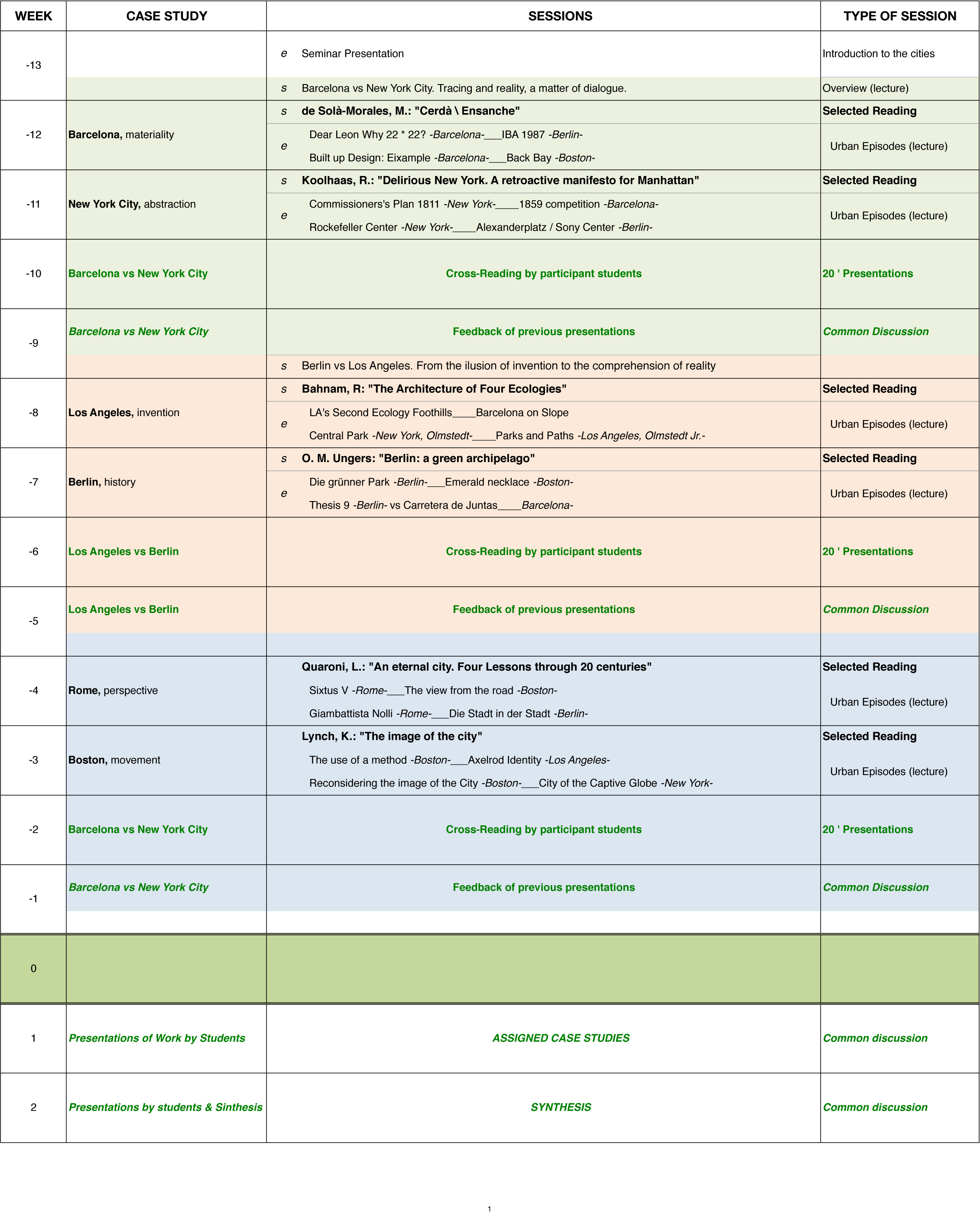
Contents
|
4
|
Evaluation
All students will be required to prepare three mid-term presentations and one final research work: 1. Mid-term presentations will develop both in writing and graphics one of the urban episodis proposed by the instructor in weeks 2&3. Teams of one or two membres will prepare the presentation. Required formats are: - One power point presentation(20’) - One panel in format Arch D containing original graphics and synthetic texts. Graphics (models, drawings, photomontages,etc…) must be original, thus meaning that at least a certain manipulation of existint graphics is required. Texts cannot exceed 1000 words (including aphorisms and captions). 2. Final research work will be focused on the intentional reading of one of the analyzed cities. The chosen case‐study will be graphically described in its three basic components: physical, formal and perceived space. Using the training and knowledge acquired during the seminar, a synthetic description is here expected. This presentation will be done individually or, exceptionally, in teams of two members. Required formats are: -One power point presentation (10’) - One panel in format Arch E containing original graphics and synthetic texts. Graphics (models, drawings, photomontages, etc…) must be original, thus meaning that at least a certain manipulation of existint graphics is required. Texts cannot exceed 2000 words (including aphorisms and captions). Proposed assignments weighting Mid-term presentations: 15% each Final presentation: 55% Student participation in all seminar meetings and field trips is mandatory. Less than full active participation will be reflected in the student’s course grade.The participation grade will be based on two equally weighed parts: 1) ability to demonstrate, during discussions and through actions, an understanding of and personal reflection on requiredcourse material and 2) active participation in all in-class activities. Students are responsable for completing those readings before each Meeting as well as analyzing and reflectint on their own reactions to the readings. The dynamic of the seminar requires all presentations to be done on the scheduled dates. Late assignments/presentations won’t be graded. The nature of this seminar could require participants to work in teams to complete presentations. When working in teams, please remember that team projects are supposed to be that – projects worked on and completed by all membres of a team. In this course, team assignments will be graded; however, all team membres will not necessarily receive the same grade for the assignment. At the end of the assignment, team membres can be asked to assess the work that they themselves have accomplished as well as the work that other membres of their team have accomplished. |
Bibliography
Axelrod, J (2009) “Inventing Autopia. Dreams and visionsof the modern metròpolis in jazz age Los Angeles”, University of California Press.
Bacon, E. (1976) “Design of cities”, Penguin Books.
Ballon, H. (2012) “The Greatest Grid. The Master Plan of Manhattan, 1811-2011”, The Museum of the City of New York.
Banerjee, T.& Southworth M. (2002) “City Sense and City Design. Writings and projects of Kevin Lynch”, MIT Press
Banham, R. (2000) “Los Angeles. The Architecture of four ecologies”, University of California Press.
Hertweck, F.& Marot, S. (2013). “The City in the City. A manifesto (1977) by Oswald Mathias Ungers and Rem Koolhaas”, Lars Müller Publishers.
Koolhaas, R. (1994) “Delirious New York. A retroactive manifesto for Manhattan”, Monacelli Press.
Quaroni, L. (2008) “Una Ciudad eterna. Cuatro lecciones de veintisiete siglos. An eternal city. Four lessons of twenty-seven centuries”, Fundación Caja de Arquitectos.
Sennet, R.(1992), “The conscience of the eye. The Design and Social Life of Cities”, W.W. Norton and Company.
De Sola-Morales, M. (2008) “Ten Lessons on Barcelona”, COAC.
De Sola-Morales, M. (2010) “Cerda--‐Ensanche”, Edicions UPC_BarcelonaTECH.
Comparteix: